Contents
- I. Understanding the Differences: Vegan, Plant-Based, and Vegetarian
- II. The Basics of a Vegan Diet
- III. The Principles of a Plant-Based Lifestyle
- IV. Exploring the Benefits of a Vegetarian Lifestyle
- V. Key Distinctions: Veganism versus Plant-Based Eating
- VI. Debunking Myths: Clarifying Misconceptions about Vegan, Plant-Based, and Vegetarian Diets
- 1. Are all vegans the same as vegetarians?
- 2. Can you get enough protein on a vegan or plant-based diet?
- 3. Do vegans lack essential nutrients like calcium?
- 4. Is it difficult for vegans to meet their vitamin B12 requirements?
- 5. Are plant-based diets lacking in essential fatty acids?
- 6. Can a vegan or vegetarian diet support athletic performance?
- 7. Do vegans have to rely on processed foods?
- 8. Is it more expensive to follow a vegan or plant-based diet?
- VII. Frequently Asked Questions about Vegan, Plant-Based, and Vegetarian Lifestyles
- 1. What is the main difference between vegan and plant-based diets?
- 2. Are vegetarians considered vegans?
- 3. Can you be both vegetarian and vegan at the same time?
- 4. Are there any health benefits of following these lifestyles?
- 5.Can I get enough protein on a vegan or plant-based diet?
- 6. Are vegan and plant-based diets suitable for children?
- 7. Can I eat out while following these lifestyles?
- 8. Will following these lifestyles help me lose weight?
- 9. Can following a vegan lifestyle cause any nutrient deficiencies?
- 10. How long does it take for someone’s taste buds to adjust when transitioning from an omnivorous diet? The adjustment period varies from person to person. Some may adapt quickly within weeks while others may need more time. Taste buds change over time as you expose them to different flavors; thus, the transition becomes easier with experimentation and exploration of new ingredients .
I. Understanding the Differences: Vegan, Plant-Based, and Vegetarian
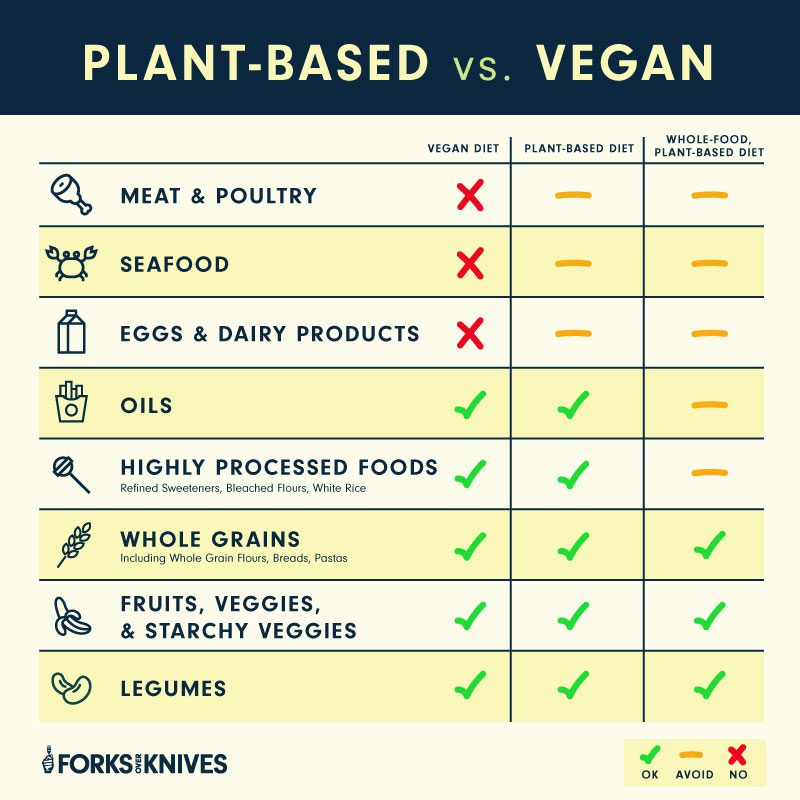
When it comes to dietary choices, there is often confusion surrounding the terms vegan, plant-based, and vegetarian. While they may seem similar at a glance, each lifestyle choice has its own unique characteristics and reasons behind them.
Veganism: A Lifestyle Committed to Animal Welfare
Veganism is more than just a diet; it’s a way of life that seeks to avoid using or exploiting animals in any form. Vegans not only abstain from consuming meat but also avoid all animal by-products such as eggs, dairy products, honey, and even gelatin derived from animal bones.
This choice stems from an ethical standpoint aimed at reducing harm to animals and promoting their well-being. By eliminating animal products entirely from their lives, vegans strive for a cruelty-free existence.
Plant-Based: Focusing on Health and Wellbeing
A plant-based diet places emphasis on consuming whole foods derived solely from plants while minimizing or eliminating processed foods altogether. This approach prioritizes health benefits rather than solely focusing on ethical concerns.
While some individuals may adopt a plant-based lifestyle due to environmental or ethical reasons as well, the primary motivation revolves around improving personal health through nutrient-dense fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains,and seeds.
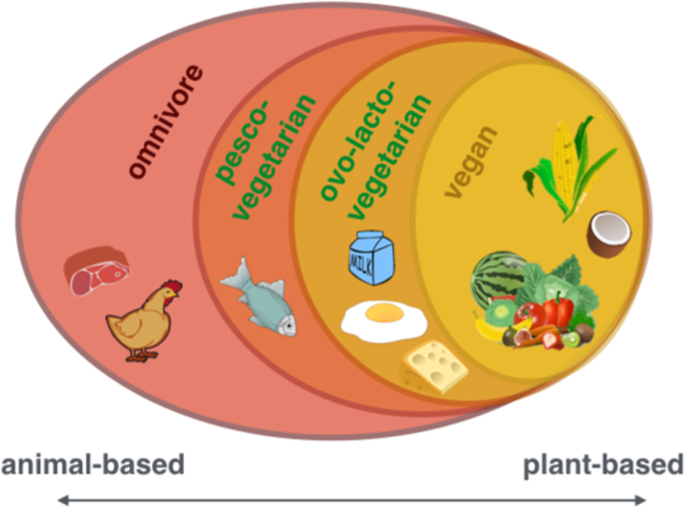
Vegetarianism: A Spectrum of Choices
The vegetarian diet encompasses various subcategories with different restrictions regarding animal-derived products:
- Lacto-Ovo Vegetarian: This group consumes both dairy products (lacto)and eggs (ovo) while avoiding meat,fish,and poultry.
- Lacto Vegetarian: Lacto vegetarians include dairy products in their diet but exclude eggs, meat, fish, and poultry.
- Ovo Vegetarian: Ovo vegetarians consume eggs but avoid all other animal-derived products.
- Pescatarian: Although not strictly vegetarian, pescatarians do not eat meat or poultry but include fish and seafood in their diet.
The reasons for adopting a vegetarian lifestyle can vary from health concerns to ethical considerations. Some individuals may choose vegetarianism due to religious beliefs or as a stepping stone towards veganism while others may simply prefer the taste of plant-based foods without completely eliminating animal products from their diets.
II. The Basics of a Vegan Diet

Switching to a vegan diet is becoming increasingly popular among individuals striving for a healthier lifestyle and a more sustainable planet. A vegan diet eliminates all animal-based products, including meat, dairy, eggs, and honey. Instead, it focuses on plant-based foods that provide essential nutrients without compromising on taste or satisfaction.
1. Plant-Based Protein Sources
Contrary to common misconceptions, vegans can easily meet their daily protein requirements through various plant-based sources. Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are an excellent choice for protein intake. Additionally, tofu and tempeh made from soybeans offer versatile options in cooking. Other protein-rich foods include quinoa, chia seeds, nuts (such as almonds and walnuts), and whole grains.
2. Essential Nutrients for Vegans
Vegans need to pay attention to certain nutrients that may be lacking in their diet due to the exclusion of animal products. These include vitamin B12—which is predominantly found in animal-derived foods—and omega-3 fatty acids typically obtained from fish oil. Vegans can obtain these nutrients through supplements or fortified plant-based sources like nutritional yeast for vitamin B12 and flaxseeds or algae oil for omega-3s.
3. Building Balanced Meals
A balanced vegan meal should consist of carbohydrates (such as whole grains or starchy vegetables), proteins (legumes or tofu), healthy fats (avocado or olive oil), and an array of colorful vegetables providing essential vitamins and minerals. It’s important to ensure variety in your meals by incorporating different fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes into your diet regularly.
4. Vegan Alternatives
The growing popularity of veganism has led to the availability of a wide range of plant-based alternatives to traditional animal-based products. For example, almond milk, soy milk, and oat milk can replace dairy milk in most recipes. Similarly, there are numerous plant-based meat substitutes made from ingredients like jackfruit, seitan, or mushrooms that provide texture and taste similar to their animal counterparts.
5. Benefits of a Vegan Diet
Adopting a vegan diet offers several benefits for both individuals and the environment. Plant-based diets have been linked to reduced risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Additionally, by eliminating animal products from your plate, you contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and conserving water resources—making it an environmentally friendly choice.
A vegan diet focuses on consuming only plant-based foods while excluding all animal-derived products. It offers ample opportunities for meeting protein requirements through legumes and other sources while ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients through supplements or fortified foods. By building balanced meals with diverse ingredients and incorporating vegan alternatives into your diet, you can enjoy the numerous health benefits associated with this lifestyle choice while contributing positively towards sustainability.
III. The Principles of a Plant-Based Lifestyle
Adopting a plant-based lifestyle involves making conscious choices to prioritize plant-derived foods while minimizing or eliminating animal products from your diet. This approach offers numerous health benefits, reduces environmental impact, and promotes animal welfare. The principles of a plant-based lifestyle are rooted in the belief that nature provides an abundance of nutritious foods that can sustain and nourish our bodies.
1. Embrace Whole Foods
A key principle of a plant-based lifestyle is consuming whole foods in their most natural form. This means opting for fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds instead of heavily processed alternatives. Whole foods are rich in essential nutrients like vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber that support overall well-being.
2. Prioritize Variety and Balance
Diversity is crucial when following a plant-based lifestyle to ensure you obtain all necessary nutrients. By embracing different colors, flavors, textures, and types of plants in your diet regularly – such as leafy greens one day or berries the next – you can benefit from an array of vitamins and minerals while avoiding monotony.
3. Opt for Plant Proteins
Sources like beans, lentils tofu tempeh chickpeas quinoa chia seeds hemp seeds provide ample protein which is vital for various bodily functions including muscle repair growth hormone production enzyme synthesis immune system support also helps keep you feeling satisfied after meals reducing cravings for unhealthy snacks.
4. Include Healthy Fats
Incorporate healthy fats into your plant-based diet such as avocados nuts seeds olive oil coconut oil flaxseed oil these fats provide energy aid absorption fat-soluble vitamins promote brain function reduce inflammation help maintain healthy skin hair nails.
5. Mindful Supplementation
While a well-planned plant-based diet can meet most nutritional needs, some nutrients may require additional attention. It is advisable to monitor and supplement key nutrients like vitamin B12, omega-3 fatty acids, iron, iodine, and calcium to ensure optimal health.
6. Stay Hydrated
Maintaining proper hydration is important for overall health and well-being. Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day and incorporate hydrating plant-based beverages such as herbal teas or homemade fruit-infused waters to stay hydrated.
7. Practice Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves being present in the moment while consuming your meals. Take time to appreciate the flavors, textures, and aromas of your food. Chew slowly, savor each bite, and listen to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Incorporating these principles into your daily life can help you transition smoothly into a plant-based lifestyle while ensuring you reap its many benefits – improved health outcomes for yourself along with reduced environmental impact and compassion towards animals.
IV. Exploring the Benefits of a Vegetarian Lifestyle
A vegetarian lifestyle refers to a dietary choice that excludes the consumption of meat, poultry, and seafood while allowing for the inclusion of plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. This way of eating has gained popularity in recent years due to its numerous health benefits and positive impact on the environment.
1. Improved Heart Health
One major benefit of adopting a vegetarian lifestyle is improved heart health. Studies have shown that vegetarians tend to have lower levels of cholesterol and blood pressure compared to non-vegetarians. By eliminating high-fat animal products from their diet, vegetarians reduce their risk of developing heart disease or experiencing cardiovascular-related issues.
2. Weight Management
A vegetarian diet can be an effective way to manage weight and prevent obesity. Plant-based foods are generally lower in calories and fat while being rich in fiber which helps promote feelings of fullness and reduces overeating tendencies. Additionally, vegetarian diets are often associated with higher intakes of fruits and vegetables which are low in calories but high in essential nutrients.
3. Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases
The consumption of a variety of plant-based foods provides essential nutrients like vitamins C and E along with antioxidants that help protect against chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, arthritis, and osteoporosis among others. The abundance of phytochemicals found in fruits, vegetables, legumes aids in fighting inflammation within the body thereby reducing the risk factors associated with these diseases.
4. Environmental Sustainability
In addition to personal health benefits, adopting a vegetarian lifestyle also contributes positively towards environmental sustainability. Animal agriculture is one major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change; therefore, reducing meat consumption helps to minimize the carbon footprint. Moreover, vegetarian diets require less land, water, and energy resources compared to traditional meat-based diets.
5. Ethical Considerations
For many individuals, choosing a vegetarian lifestyle is driven by ethical considerations related to animal welfare. By avoiding the consumption of meat products, vegetarians refrain from supporting industries that often engage in practices such as factory farming or animal cruelty. This conscious choice aligns with their personal values and promotes compassion towards animals.
V. Key Distinctions: Veganism versus Plant-Based Eating
When it comes to dietary choices, there are various terms that often get used interchangeably. However, it’s important to understand the key distinctions between veganism and plant-based eating in order to make informed decisions about your lifestyle and diet.
1. Definition of Veganism
Veganism is a philosophy and lifestyle that aims to exclude all forms of animal exploitation and cruelty, not just in food choices but also in clothing, cosmetics, and other aspects of life. Vegans abstain from consuming any animal products or by-products, including meat, fish, dairy products, eggs, honey, gelatin, and more.
2. Principles of Plant-Based Eating
Plant-based eating focuses primarily on consuming whole foods derived from plants while minimizing or eliminating animal products from the diet. The emphasis is on fruits, vegetables, legumes (beans), nuts/seeds as primary sources of nutrition.
3. Motivation Behind Veganism
Vegans choose this lifestyle due to ethical concerns for animals’ welfare as well as environmental sustainability issues. They believe in minimizing harm caused to animals through their dietary choices by not supporting industries that exploit animals for food or other purposes.
4. Health Benefits of Plant-Based Eating
A plant-based diet has been associated with numerous health benefits such as lower risks of heart disease, type 2 diabetes,
obesity,
certain cancers,
high blood pressure,
and improved overall well-being.
By focusing on nutrient-dense plant foods,
individuals can ensure they consume a wide variety
of essential vitamins,minerals,
phytochemicals,and antioxidants critical for optimal health.
a) Emphasizing Whole Foods
Plant-based eating encourages the consumption of whole foods in their natural state. This means prioritizing fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds instead of processed or refined foods.
b) Flexibility with Animal Products
While veganism strictly avoids animal products altogether,
plant-based eating allows for occasional inclusion
of animal-derived foods if an individual so chooses.
The focus is on reducing animal product intake significantly,
while still maintaining a predominantly plant-centric diet.
5. Sustainability Factors
Veganism promotes sustainability by reducing greenhouse gas emissions,
land and water use associated with animal agriculture.
Plant-based eating also contributes to environmental conservation efforts by minimizing the demand for factory farming practices,
which can have detrimental effects on ecosystems and climate change.
In conclusion,Veganism encompasses a broader ethical lifestyle choice that extends beyond just dietary preferences.Plant-based eating is primarily focused on food choices but allows flexibility regarding occasional consumption of animal products.Key distinctions between veganism and plant-based eating come down to personal beliefs,motivations,and the extent to which one chooses to exclude or include animal products in their diet.
VI. Debunking Myths: Clarifying Misconceptions about Vegan, Plant-Based, and Vegetarian Diets
There are many misconceptions surrounding vegan, plant-based, and vegetarian diets. It’s important to debunk these myths to gain a better understanding of the differences between these dietary choices.
1. Are all vegans the same as vegetarians?
No, there is a distinction between vegans and vegetarians. While both groups abstain from consuming meat, vegetarians may still consume animal by-products such as dairy and eggs. Vegans, on the other hand, avoid all animal products in their diet and lifestyle.
2. Can you get enough protein on a vegan or plant-based diet?
Absolutely! Contrary to popular belief, it is entirely possible to meet your protein needs on a vegan or plant-based diet. There are numerous plant sources of protein available such as legumes (beans and lentils), tofu, tempeh, seitan, quinoa, chia seeds, hemp seeds, and more.
3. Do vegans lack essential nutrients like calcium?
Vegans can obtain calcium from non-dairy sources such as leafy green vegetables (kale and broccoli), fortified plant milk (almond or soy milk), tofu made with calcium sulfate, tahini (sesame seed paste), almonds or almond butter.
4. Is it difficult for vegans to meet their vitamin B12 requirements?
Vitamin B12 is primarily found in animal products; therefore it can be challenging for vegans to obtain adequate amounts solely through food sources alone. However,vitamin B12 supplements are widely available for those following a vegan or vegetarian lifestyle.
5. Are plant-based diets lacking in essential fatty acids?
Plant-based diets can provide sufficient amounts of essential fatty acids, such as omega-3 and omega-6. Foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts, and algae-derived supplements are excellent sources of these important nutrients.
6. Can a vegan or vegetarian diet support athletic performance?
A well-planned vegan or vegetarian diet can certainly support athletic performance. Many successful athletes follow plant-based diets and achieve great results. Proper meal planning to meet energy needs and ensure adequate intake of protein, carbohydrates, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals is crucial for optimal performance.
7. Do vegans have to rely on processed foods?
No! While there are many delicious plant-based processed foods available in the market today like mock meats and dairy-free alternatives; following a whole-foods approach is entirely possible on a vegan or vegetarian diet by consuming fruits, vegetables,nuts Andamp; seeds,and whole grains.
8. Is it more expensive to follow a vegan or plant-based diet?
The cost of following a vegan or plant-based diet depends on various factors including location and personal food choices.While some specialty products may be pricier,the majority of staples like beans,rice,pasta,and fresh produce are affordable options.Making meals from scratch using whole ingredients can also help keep costs down.
In summary, debunking myths surrounding veganism,pant based Andamp; vegetarianism allows us to gain clarity regarding these dietary choices.Whether you’re considering adopting one yourself or simply seeking accurate information,it’s important to understand the nuances between them while dispelling misconceptions that may exist
VII. Frequently Asked Questions about Vegan, Plant-Based, and Vegetarian Lifestyles
When it comes to dietary choices, vegan, plant-based, and vegetarian lifestyles have gained significant popularity in recent years. However, confusion often arises regarding the differences between these three options. To help clear things up, here are some frequently asked questions about veganism, plant-based diets, and vegetarianism.
1. What is the main difference between vegan and plant-based diets?
The main difference lies in the motivation behind each choice. Vegans follow a lifestyle that avoids all animal products due to ethical reasons associated with animal rights or environmental concerns. On the other hand, those following a plant-based diet primarily focus on consuming whole foods derived from plants for health benefits.
2. Are vegetarians considered vegans?
No, vegetarians are not considered vegans as they still consume certain animal products such as eggs or dairy but exclude meat from their diet.
3. Can you be both vegetarian and vegan at the same time?
No; being both vegetarian and vegan would contradict each other since vegetarians can consume dairy or eggs while vegans avoid all animal-derived products entirely.
4. Are there any health benefits of following these lifestyles?
Absolutely! Research has shown that adopting a well-planned vegan or plant-based diet can lead to numerous health benefits like reduced risk of heart disease, lower cholesterol levels, improved digestion, increased energy levels,
5.Can I get enough protein on a vegan or plant-based diet?
Absolutely! While it may require more careful planning compared to omnivorous diets,
vegans and those following a plant-based lifestyle can obtain ample protein through sources such as legumes, quinoa, tofu, tempeh, and seitan.
6. Are vegan and plant-based diets suitable for children?
If properly planned to ensure adequate nutrient intake, both vegan and plant-based diets can provide all the necessary nutrients for children’s growth and development. However, it is recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure proper nutrition.
7. Can I eat out while following these lifestyles?
Absolutely! Many restaurants now offer vegan or plant-based options on their menus due to increasing demand. Moreover,
you can always inform the waiter about your dietary preferences so they can accommodate your needs.
8. Will following these lifestyles help me lose weight?
Veganism, plant-based diets, and vegetarianism can contribute to weight loss if you focus on consuming whole foods rich in fiber and nutrients while minimizing processed foods high in added sugars or unhealthy fats.
9. Can following a vegan lifestyle cause any nutrient deficiencies?
If well-planned with attention given to meeting nutrient needs through a varied diet,
vegan lifestyles are generally nutritionally sufficient.
However,
it is important to pay special attention
to certain nutrients like vitamin B12,
iron,
calcium,
and omega-3 fatty acids
.
10. How long does it take for someone’s taste buds to adjust when transitioning from an omnivorous diet?
The adjustment period varies from person to person.
Some may adapt quickly within weeks while others may need more time.
Taste buds change over time
as you expose them
to different flavors;
thus,
the transition becomes easier with experimentation
and exploration of new ingredients
.
Some may adapt quickly within weeks while others may need more time.
Taste buds change over time
as you expose them
to different flavors;
thus,
the transition becomes easier with experimentation
and exploration of new ingredients

Nicole Allen is a highly skilled and passionate content writer, specializing in SEO. With a strong command of the English language, Nicole has honed her writing skills to deliver engaging and informative content to her readers. Her educational background includes a Bachelor’s degree in English Literature from the University of California, Berkeley. Nicole’s love for veganism and sustainable living has fueled her dedication to creating content that promotes a cruelty-free lifestyle. Her extensive knowledge of plant-based nutrition and ethical consumerism allows her to craft compelling articles that inspire and educate readers on the benefits of embracing a vegan lifestyle.
